LC Oscillations
LC Oscillations: Overview
In this topic, we will learn about LC oscillations in detail with diagrams. It explains the reason for unrealistic LC oscillations. It also discusses the analogies between mechanical and electrical quantities.
Important Questions on LC Oscillations
In an LC oscillating circuit with and , the maximum charge of capacitor is . Maximum current through the circuit will be
In the circuit shown in figure is open and, and are closed. The circuit is in steady state. At time , switch , is closed and and are opened simultaneously. ,
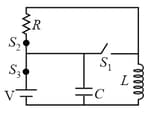
Find the maximum charge that will appear on the capacitor at any time
A capacitor of capacitance is charged by a battery. Charged capacitor is now connected to an inductor of inductance . Then find the current in the circuit when one third energy stored in capacitor converts into the energy stored in inductor.
In L.C oscillation, maximum current in the inductor can be . If at any instant, electric energy and magnetic energy associated with circuit is equal, then current in the inductor at that instant is
In an L-C oscillation maximum charge on capacitor can be . If at any instant electrical energy is th of the magnetic energy then the charge on capacitor at that instant is
Two capacitors of capacitance and are given charges and respectively as shown in figure. If switch is closed what will be maximum current through inductor.
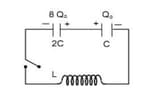
In an circuit shown in the figure, At time charge in the capacitor is and it is decreasing at a rate of Choose the correct statements.
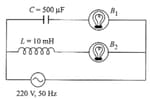
In the circuit shown in figure, if both the bulbs and are identical, then
A radio receiver can tune over the frequency range to . If the tunable circuit has a fixed inductor, what must be the range over which the capacitor must be tuned? (You can use )
We connect a charge capacitor to an inductor the electric current and charge on the capacitor in the circuit undergoes LC oscillations.
An resonant circuit contains a capacitor and an inductor of It is coupled to an antenna. Wavelength of radiated electromagnetic wave is
A capacitor is charged to . This charged capacitor is connected across a coil, so that oscillations occur. The maximum current in the coil is:-
In an circuit shown in figure, and . At time , charge on the capacitor is coulomb and it is decreasing with rate of . Then choose the correct statement.
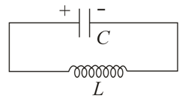
The natural frequency of the circuit is (in ),
In an LC oscillator circuit L = 10 mH, C = 40µF. If initially at t = 0 the capacitor is fully charged with 4µC then find the current in the circuit when the capacitor and inductor share equal energies.
The diagram shows a capacitor C and a resistor R connected in series to an AC source, V1 and V2 are voltmeters and A is an ammeter. Consider now the following statements :
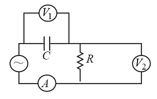
(I) Readings in A and V1 are always in phase
(II) Readings in A and V2 are always in phase
(III) Reading in V1 is ahead with reading in V2
Which of these statements are is correct :
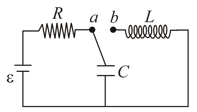
The switch in the circuit pictured is in position a for a long time. At t = 0 the switch is moved from a to b. The current through the inductor will reach its first maximum after moving the switch in a time : -
A LC circuit is in the state of resonance. if C = 0.1 µF and L = 0.25 henry. Neglecting ohmic resistance of circuit what is the frequency of oscillations :
